Background:
Aggressive hematological malignancies in relapsed/refractory setting bear a dire prognosis with low cure rates and short survival. Matching these patients to therapies is challenged by complexity due to spatial and temporal tumor evolution and incomplete understanding of genotype to phenotype correlations. Direct functional testing could address these impediments. The EXALT trial is an interventional, one-arm study designed to assess the clinical value of next generation functional drug screening (ngFDS). An interim analysis on 17 patients suggested a clinical benefit (Snijder et al., Lancet Hematol. 2017).
Methods:
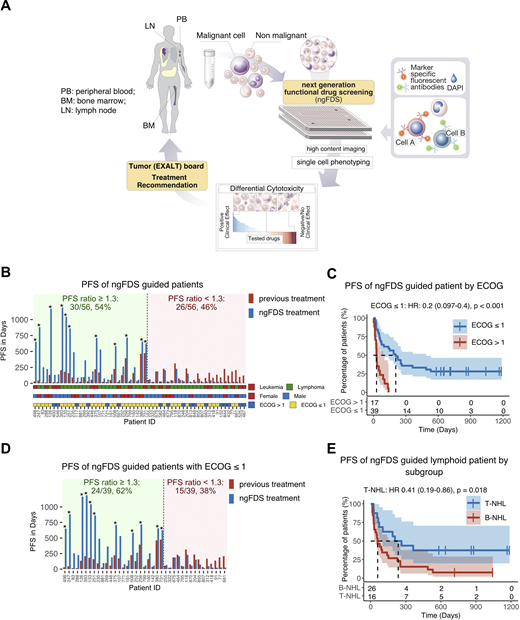
We applied image-based ngFDS to quantify differential ex-vivo sensitivity of primary patient tumor cells to respective non-tumor cells towards 136 small molecule drugs, including EMA approved for any indication or experimental. We screened bone marrow, peripheral blood or lymph node material from 143 patients who suffered from late stage aggressive hematological malignancies (acute leukemias, aggressive B- and T-cell lymphomas) , discussed the results in a multidisciplinary tumor board and recommended treatments to physicians (A). The primary endpoint of this study was the percentage of patients reaching a PFS-ratio (PFS(ngFDS treatment)/PFS(previous treatment)) of ≥1.3 with an H0 hypothesis < 15% patients. The secondary endpoint was overall response rate (ORR) defined as proportion of patients reaching complete remission (CR) or partial remission (PR). Additionally, we performed a post hoc analysis to evaluate the matching of ngFDS to drugs used in actual treatment (matching score of received treatment).
Results:
56 (39%) patients were evaluable and treated according to ngFDS based recommendations. With 30 of 56 (54%) ngFDS guided patients experiencing a PFS ratio of ≥1.3, the primary study endpoint was reached. 11 patients (37%) had ongoing response at censoring date (B). The median follow-up was 718 days. The median number of days from sampling to treatment was 21 (range 4-77). The ngFDS treatment regimens consisted of a median of 2 drugs (range: 1-6). ORR was 55% for all evaluable ngFDS treated patients, 60% for the lymphoid subgroup and 41% for the myeloid subgroup. Patients on ngFDS guided treatment with performance status ECOG ≤ 1 had a median PFS of 207 days compared to a median PFS of 29 days for patients with higher ECOG (p < 0.001, C). 24 of 39 (62%) patients with ECOG ≤ 1 had a PFS ratio of ≥1.3 (D). In disease specific subgroup analysis median PFS of T-cell lymphoma patients was 235 days versus 60 days for B-cell lymphoma patients (p = 0.018, E). Age (≤60 vs. >60), sex, lineage (myeloid vs. lymphoid), number of previous treatment lines (≤2 vs. >2), and clinical presentation (leukemia vs. lymphoma) did not have an impact on PFS of ngFDS guided treatment. Post hoc analysis including additional 17 non-ngFDS treated patients demonstrated that only patients receiving treatment with a positive ngFDS matching score demonstrated clinical benefit (HR: 0.53, p=0.005; vs. HR: 1.4, p=0.4). ngFDS matched treatments resulted in higher PFS for patients with tumor samples that had a cancer cell fraction of 10-50% in comparison to patients with samples of lower or higher cancer cell percentage (HR:0.35, p=0.01).
Conclusion:
ngFDS could be integrated in the routine clinical work flow. ngFDS guided treatments led to high rates of PFS prolongation compared to previous treatments of individual patients. ngFDS guided treatment is feasible and effective in patients with late stage aggressive hematological malignancies. These results prompted a prospective randomized trial comparing treatment guidance based on ngFDS or comprehensive genomic profiling or physician's choice (EXALT-2 trial, NCT04470947).
Vladimer:Allcyte GmbH: Current Employment, Current equity holder in private company, Other: Founder. Jaeger:Karyopharm: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS/Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; True North: Honoraria, Research Funding; Miltenyi: Consultancy, Honoraria; CDR Life AG: Consultancy, Research Funding; F. Hoffmann-La Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding; Infinity: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria. Krall:Allcyte GmbH: Current Employment, Current equity holder in private company, Other: Founder. Valent:Allcyte GmbH: Research Funding; Cellgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria. Wolf:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding. Zielinski:MSD: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Imugene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Ariad: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Merrimack: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Merck KGaA: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Fibrogen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Tesaro: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Shire: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Eli Lilly: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Athenex: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Superti-Furga:Allcyte GmbH: Current equity holder in private company, Other: Founder. Snijder:Allcyte GmbH: Current equity holder in private company, Other: Founder. Staber:Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene/ BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria; msd: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal